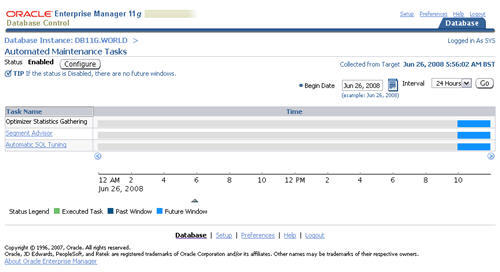
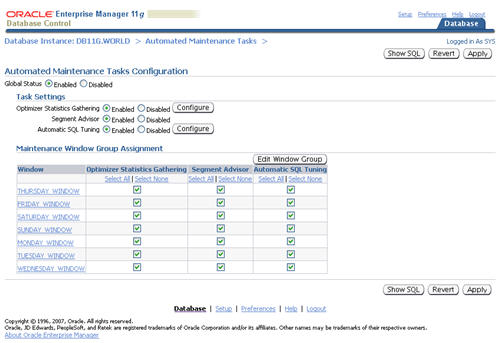
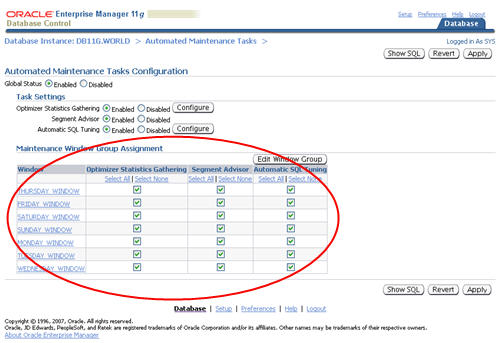
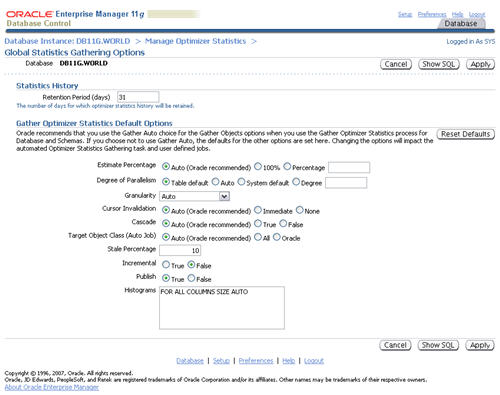
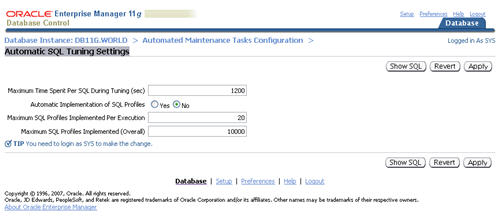
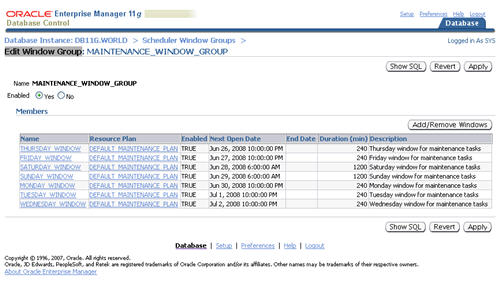
In previous database versions, new optimizer statistics were automatically published when they were gathered. In 11g this is still the default action, but you now have the option of keeping the newly gathered statistics in a pending state until you choose to publish them.
The DBMS_STATS.GET_PREFS function allows you to check 'PUBLISH' attribute to see if statistics are automatically published. The default value of TRUE means they are automatically published, while FALSE indicates they are held in a pending state.
SQL> SELECT DBMS_STATS.get_prefs('PUBLISH') FROM dual;
DBMS_STATS.GET_PREFS('PUBLISH')
-------------------------------------------
TRUE
1 row selected.
The 'PUBLISH' attribute is reset using the DBMS_STATS.SET_TABLE_PREFS procedure.
-- New statistics for SCOTT.EMP are kept in a pending state.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.set_table_prefs('SCOTT', 'EMP', 'PUBLISH', 'false');
-- New statistics for SCOTT.EMP are published immediately.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.set_table_prefs('SCOTT', 'EMP', 'PUBLISH', 'true');
[DBAALLUSER]_TAB_PENDING_STATS and
[DBAALLUSER]_IND_PENDING_STATS views.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.publish_pending_stats(NULL, NULL);
-- Publish pending statistics for a specific object.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.publish_pending_stats('SCOTT','EMP');
-- Delete pending statistics for a specific object.
EXEC DBMS_STATS.delete_pending_stats('SCOTT','EMP');
Pending statistics can be transfered between database by exporting this using the DBMS_STATS.EXPORT_PENDING_STATS procedure.
DECLARE
l_cg_name VARCHAR2(30);
BEGIN
l_cg_name := DBMS_STATS.create_extended_stats(ownname => 'SCOTT',
tabname => 'EMP',
extension => '(JOB,DEPTNO)');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
The column group name is returned using the SHOW_EXTENDED_STATS_NAME function.
-- Display the name of the columnn group.
SELECT DBMS_STATS.show_extended_stats_name(ownname => 'SCOTT',
tabname => 'EMP',
extension =>'(JOB,DEPTNO)')AS cg_name
Manually created column groups can be deleted using the DROP_EXTENDED_STATS procedure.
-- Drop the columnn group.
BEGIN
dbms_stats.drop_extended_stats(ownname => 'SCOTT',
tabname => 'EMP',
extension => '(JOB,DEPTNO)');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Setting the METHOD_OPT parameter to "FOR ALL COLUMNS SIZE AUTO" allows the GATHER_% procedures to gather statistics on all existing column groups for the specified object.
BEGIN
DBMS_STATS.gather_table_stats(
'SCOTT',
'EMP',
method_opt => 'for all columns size auto');
END;
/
Alternatively, set the METHOD_OPT parameter to "FOR COLUMNS (column-list)" and the group will automatically be created during the statistics gathering.
BEGIN
DBMS_STATS.gather_table_stats(
'SCOTT',
'EMP',
method_opt => 'for columns (job,mgr)');
END;
/
The [DBAALLUSER]_STAT_EXTENSIONS views display information about the multi-column statistics.
COLUMN extension FORMAT A30
SELECT extension_name, extension
FROM dba_stat_extensions
WHERE table_name = 'EMP';
EXTENSION_NAME EXTENSION
------------------------------ ------------------------------
SYS_STU3VG629OEYG6FN0EKTGV_HQ6 ("JOB","DEPTNO")
SYS_STULPA1A#B6YL4KQ59DQO3OADQ ("JOB","MGR")
2 rows selected.
COLUMN col_group FORMAT A30
SELECT e.extension col_group,
t.num_distinct,
t.histogram
FROM dba_stat_extensions e
JOIN dba_tab_col_statistics t
ON e.extension_name=t.column_name
AND t.table_name = 'EMP';
COL_GROUP NUM_DISTINCT HISTOGRAM
------------------------------ ------------ ---------------
("JOB","DEPTNO") 9 FREQUENCY
("JOB","MGR") 8 FREQUENCY
2 rows selected.
Expression Statistics
The optimizer has no idea what the affect of applying a function to column has on the selectivity of the column. Using a similar method to multi-column statistics, we can gather expression statistics to provide more information.
Expression statistics can be created explicitly using the CREATE_EXTENDED_STATS procedure, or implicitly by specifying the expression in the METHOD_OPT parameter of the GATHER_% procedures when gathering statistics.
DECLARE
l_cg_name VARCHAR2(30);
BEGIN
-- Explicitly created.
l_cg_name := DBMS_STATS.create_extended_stats(ownname => 'SCOTT',
tabname => 'EMP',
extension => '(LOWER(ENAME))');
-- Implicitly created.
DBMS_STATS.gather_table_stats(
'SCOTT',
'EMP',
method_opt => 'for columns (upper(ename))');
END;
/
Setting the METHOD_OPT parameter to "FOR ALL COLUMNS SIZE AUTO" allows the GATHER_% procedures to gather existing expression statistics.
BEGIN
DBMS_STATS.gather_table_stats(
'SCOTT',
'EMP',
method_opt => 'for all columns size auto');
END;
/
The [DBAALLUSER]_STAT_EXTENSIONS views display information about the expression statistics, as well as the multi-column statistics.
COLUMN extension FORMAT A30
SELECT extension_name, extension
FROM dba_stat_extensions
WHERE table_name = 'EMP';
EXTENSION_NAME EXTENSION
------------------------------ ------------------------------
SYS_STU3VG629OEYG6FN0EKTGV_HQ6 ("JOB","DEPTNO")
SYS_STULPA1A#B6YL4KQ59DQO3OADQ ("JOB","MGR")
SYS_STU2JLSDWQAFJHQST7$QK81_YB (LOWER("ENAME"))
SYS_STUOK75YSL165W#_X8GUYL0A1X (UPPER("ENAME"))
4 rows selected.
SQL>
COLUMN col_group FORMAT A30
SELECT e.extension col_group,
t.num_distinct,
t.histogram
FROM dba_stat_extensions e
JOIN dba_tab_col_statistics t ON e.extension_name=t.column_name
AND t.table_name = 'EMP';
COL_GROUP NUM_DISTINCT HISTOGRAM
------------------------------ ------------ ---------------
("JOB","DEPTNO") 9 NONE
("JOB","MGR") 8 NONE
(LOWER("ENAME")) 14 NONE
(UPPER("ENAME")) 14 NONE
4 rows selected.
Expression statistics are dropped using the DROP_EXTENDED_STATS procedure.
-- Drop the columnn group.
BEGIN
dbms_stats.drop_extended_stats(ownname => 'SCOTT',
tabname => 'EMP',
extension => '(UPPER(ENAME))');
END;
/
PL/SQL procedure successfully completed.
Enhanced Statistics Collection for Partitioned Objects
Oracle 11g includes improvements to statistics collection for partitioned objects so untouched partitions are not rescanned. This significantly increases the speed of statistics collection on large tables where some of the partitions contain static data. Where partition exchange load (PEL) is used to add data to the a table, only the newly added partition must be scanned to update the global statistics.